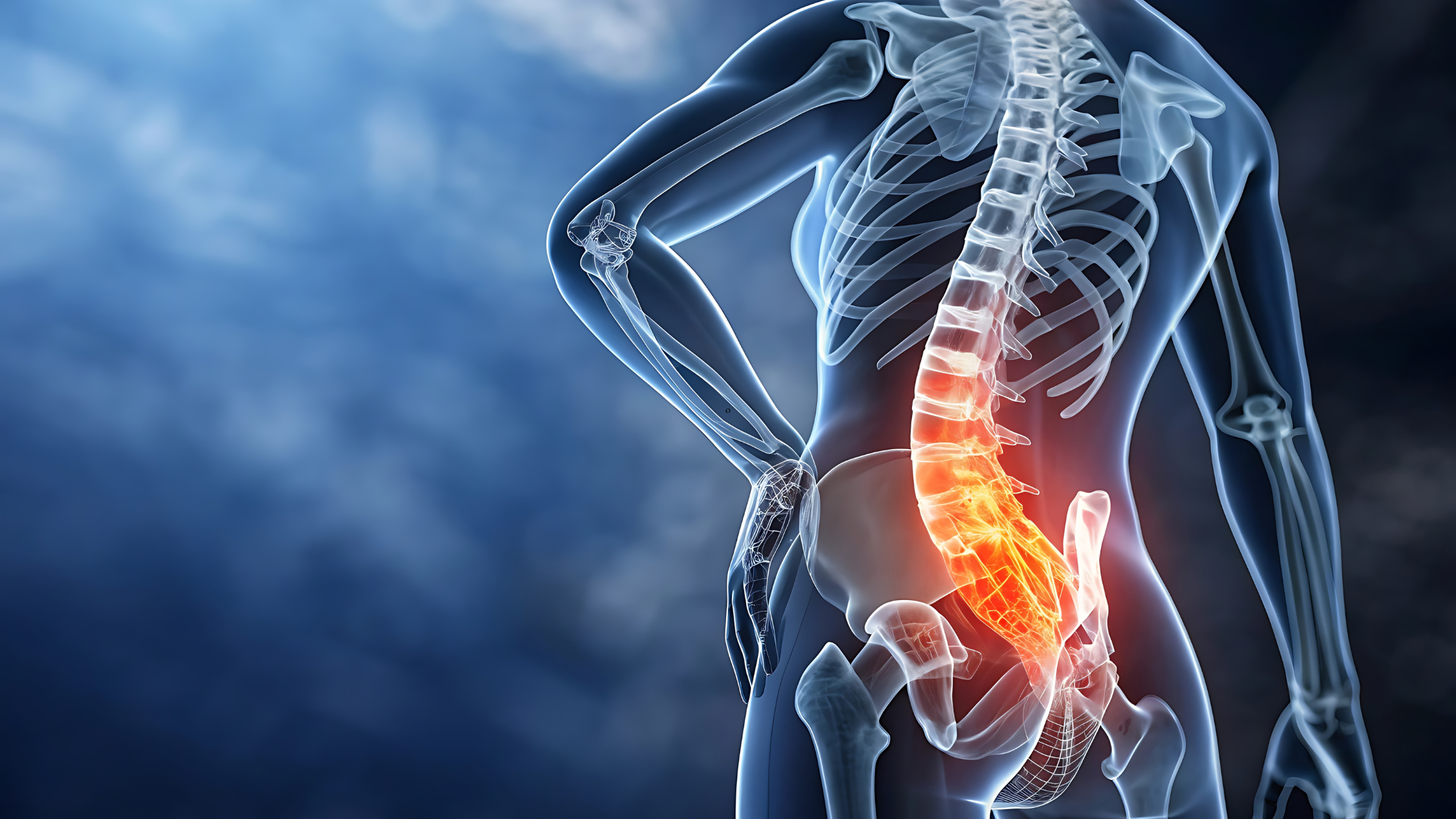
The sacroiliac (SI) joints play a vital role in connecting your spine to your pelvis and supporting your body during movement. When these joints become inflamed or irritated, it can lead to significant pain and stiffness that interferes with everyday activities. Understanding SI joint pain can help you recognize the signs early and seek proper treatment.
What Is the SI Joint?
The SI joints are located on each side of the lower spine, where the sacrum (the base of the spine) meets the iliac bones of the pelvis. These joints act as shock absorbers, transferring the weight and forces between your upper body and legs. Though they allow for very limited movement, they are critical for stability and balance.
Common Causes of SI Joint Pain
- Injury or trauma: A fall, car accident, or sports injury can disrupt the alignment or function of the SI joint.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and added pelvic stress during pregnancy can loosen the ligaments supporting the joint.
- Arthritis: Degenerative or inflammatory arthritis, such as osteoarthritis or ankylosing spondylitis, can affect the SI joint.
- Uneven leg length or gait problems: Imbalances in how you walk or stand can strain one side of the SI joint over time.
- Repetitive stress: Jobs or activities that involve frequent bending, twisting, or lifting can irritate the joint.
Recognizing the Symptoms
SI joint pain can be mistaken for other lower back or hip problems because of its location. Common symptoms include:
- Pain in the lower back, buttocks, or hips, often on one side
- Pain that radiates to the groin, thigh, or upper leg
- Stiffness, especially after sitting or standing for long periods
- Pain that worsens when climbing stairs, running, or transitioning from sitting to standing
- Relief when lying down or changing positions
A physician can confirm SI joint involvement through a physical exam, imaging studies, or diagnostic injections.
Diagnosing SI Joint Dysfunction
Diagnosis often includes:
- Physical exam tests: Such as the FABER or Gaenslen’s test to pinpoint SI joint pain.
- Imaging studies: X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans to rule out other spinal or hip conditions.
- Diagnostic injections: A local anesthetic may be injected into the SI joint to confirm it as the pain source—if pain relief follows, the diagnosis is likely correct.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the cause and severity of your symptoms but often begins conservatively:
- Rest and activity modification: Avoiding activities that aggravate the pain can help reduce inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Exercises to strengthen the core and stabilize the pelvis can relieve joint stress.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory medications may reduce pain and swelling.
- Injections: Corticosteroid or regenerative medicine injections (such as PRP) can provide longer-lasting relief.
- SI joint fusion: In severe or chronic cases where conservative care fails, minimally invasive SI joint fusion may be recommended to stabilize the joint and relieve pain.
When to Seek Help
If lower back or hip pain persists for more than a few weeks, or if it interferes with walking, sleep, or daily activities, it’s important to seek professional evaluation. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent worsening pain and improve quality of life.
The Takeaway
SI joint pain is a common yet often overlooked source of lower back and pelvic discomfort. With proper diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan, most people can find lasting relief and return to their normal routines. If you suspect your pain may be coming from the SI joint, consult a pain specialist or orthopedic provider for an accurate evaluation and targeted treatment options.

